The Universal Debating Project offers a "simple" pro, and con approach towards data. However, there are other ways of presenting information as is already indicated in this blog. Blogger Ref http://www.p2pfoundation.net/Universal_Debating_Project
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from Structured data)
A data model organizes data elements and standardizes how the data elements relate to one another. Since data elements document real life people, places and things and the events between them, the data model represents reality, for example a house has many windows or a cat has two eyes. Computers are used for the accounting of these real life things and events and therefore the data model is a necessary standard to ensure exact communication between human beings.
 Data models are often used as an aid to communication between the business people defining the requirements for a computer system and the technical people defining the design in response to those requirements. They are used to show the data needed and created by business processes.
Data models are often used as an aid to communication between the business people defining the requirements for a computer system and the technical people defining the design in response to those requirements. They are used to show the data needed and created by business processes.
Precise accounting and communication is a large expense and organizations traditionally paid the cost by having employees translate between themselves on an ad hoc basis. In critical situations such as air travel, healthcare and finance, it is becoming commonplace that the accounting and communication must be precise and therefore requires the use of common data models to obviate risk.
According to Hoberman (2009), "A data model is a wayfinding tool for both business and IT professionals, which uses a set of symbols and text to precisely explain a subset of real information to improve communication within the organization and thereby lead to a more flexible and stable application environment."[2]
A data model explicitly determines the structure of data. Data models are specified in a data modeling notation, which is often graphical in form.[3]
A data model can be sometimes referred to as a data structure, especially in the context of programming languages. Data models are often complemented by function models, especially in the context of enterprise models.
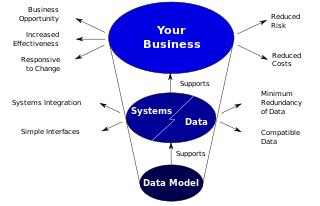 The main aim of data models is to support the development of information systems by providing the definition and format of data. According to West and Fowler (1999) "if this is done consistently across systems then compatibility of data can be achieved. If the same data structures are used to store and access data then different applications can share data. The results of this are indicated above. However, systems and interfaces often cost more than they should, to build, operate, and maintain. They may also constrain the business rather than support it. A major cause is that the quality of the data models implemented in systems and interfaces is poor".[4]
The main aim of data models is to support the development of information systems by providing the definition and format of data. According to West and Fowler (1999) "if this is done consistently across systems then compatibility of data can be achieved. If the same data structures are used to store and access data then different applications can share data. The results of this are indicated above. However, systems and interfaces often cost more than they should, to build, operate, and maintain. They may also constrain the business rather than support it. A major cause is that the quality of the data models implemented in systems and interfaces is poor".[4]
A data model explicitly determines the structure of data or structured data. Typical applications of data models include database models, design of information systems, and enabling exchange of data. Usually data models are specified in a data modeling language.[3]
Communication and precision are the two key benefits that make a data model important to applications that use and exchange data. A data model is the medium which project team members from different backgrounds and with different levels of experience can communicate with one another. Precision means that the terms and rules on a data model can be interpreted only one way and are not ambiguous.[2]
A data model can be sometimes referred to as a data structure, especially in the context of programming languages. Data models are often complemented by function models, especially in the context of enterprise models.
 A data model instance may be one of three kinds according to ANSI in 1975:[5]
A data model instance may be one of three kinds according to ANSI in 1975:[5]
In the 1960s data modeling gained more significance with the initiation of the management information system (MIS) concept. According to Leondes (2002), "during that time, the information system provided the data and information for management purposes. The first generation database system, called Integrated Data Store (IDS), was designed by Charles Bachman at General Electric. Two famous database models, the network data model and the hierarchical data model, were proposed during this period of time".[10] Towards the end of the 1960s Edgar F. Codd worked out his theories of data arrangement, and proposed the relational model for database management based on first-order predicate logic.[11]
In the 1970s entity relationship modeling emerged as a new type of conceptual data modeling, originally proposed in 1976 by Peter Chen. Entity relationship models were being used in the first stage of information system design during the requirements analysis to describe information needs or the type of information that is to be stored in a database. This technique can describe any ontology, i.e., an overview and classification of concepts and their relationships, for a certain area of interest.
In the 1970s G.M. Nijssen developed "Natural Language Information Analysis Method" (NIAM) method, and developed this in the 1980s in cooperation with Terry Halpin into Object-Role Modeling (ORM).
Bill Kent, in his 1978 book Data and Reality[12] compared a data model to a map of a territory, emphasizing that in the real world, "highways are not painted red, rivers don't have county lines running down the middle, and you can't see contour lines on a mountain". In contrast to other researchers who tried to create models that were mathematically clean and elegant, Kent emphasized the essential messiness of the real world, and the task of the data modeller to create order out of chaos without excessively distorting the truth.
In the 1980s according to Jan L. Harrington (2000) "the development of the object-oriented paradigm brought about a fundamental change in the way we look at data and the procedures that operate on data. Traditionally, data and procedures have been stored separately: the data and their relationship in a database, the procedures in an application program. Object orientation, however, combined an entity's procedure with its data."[13]
Several such models have been suggested. Common models include:
Data structure diagrams are an extension of the entity-relationship model (ER model). In DSDs, attributes are specified inside the entity boxes rather than outside of them, while relationships are drawn as boxes composed of attributes which specify the constraints that bind entities together. The E-R model, while robust, doesn't provide a way to specify the constraints between relationships, and becomes visually cumbersome when representing entities with several attributes. DSDs differ from the ER model in that the ER model focuses on the relationships between different entities, whereas DSDs focus on the relationships of the elements within an entity and enable users to fully see the links and relationships between each entity.
There are several styles for representing data structure diagrams, with the notable difference in the manner of defining cardinality. The choices are between arrow heads, inverted arrow heads (crow's feet), or numerical representation of the cardinality.
 A semantic data model in software engineering is a technique to define the meaning of data within the context of its interrelationships with other data. A semantic data model is an abstraction which defines how the stored symbols relate to the real world.[14] A semantic data model is sometimes called a conceptual data model.
A semantic data model in software engineering is a technique to define the meaning of data within the context of its interrelationships with other data. A semantic data model is an abstraction which defines how the stored symbols relate to the real world.[14] A semantic data model is sometimes called a conceptual data model.
The logical data structure of a database management system (DBMS), whether hierarchical, network, or relational, cannot totally satisfy the requirements for a conceptual definition of data because it is limited in scope and biased toward the implementation strategy employed by the DBMS. Therefore, the need to define data from a conceptual view has led to the development of semantic data modeling techniques. That is, techniques to define the meaning of data within the context of its interrelationships with other data. As illustrated in the figure. The real world, in terms of resources, ideas, events, etc., are symbolically defined within physical data stores. A semantic data model is an abstraction which defines how the stored symbols relate to the real world. Thus, the model must be a true representation of the real world.[14]
A data architecture describes the data structures used by a business and/or its applications. There are descriptions of data in storage and data in motion; descriptions of data stores, data groups and data items; and mappings of those data artifacts to data qualities, applications, locations etc.
Essential to realizing the target state, Data architecture describes how data is processed, stored, and utilized in a given system. It provides criteria for data processing operations that make it possible to design data flows and also control the flow of data in the system.
Data modeling is the process of learning about the data, and the data model is the end result of the data modeling process.[18]
The figure illustrates the way data models are developed and used today. A conceptual data model is developed based on the data requirements for the application that is being developed, perhaps in the context of an activity model. The data model will normally consist of entity types, attributes, relationships, integrity rules, and the definitions of those objects. This is then used as the start point for interface or database design.[4]

While data analysis is a common term for data modeling, the activity actually has more in common with the ideas and methods of synthesis (inferring general concepts from particular instances) than it does with analysis (identifying component concepts from more general ones). {Presumably we call ourselves systems analysts because no one can say systems synthesists.} Data modeling strives to bring the data structures of interest together into a cohesive, inseparable, whole by eliminating unnecessary data redundancies and by relating data structures with relationships.
A different approach is to use adaptive systems such as artificial neural networks that can autonomously create implicit models of data.
 A data structure is a way of storing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently. It is an organization of mathematical and logical concepts of data. Often a carefully chosen data structure will allow the most efficient algorithm to be used. The choice of the data structure often begins from the choice of an abstract data type.
A data structure is a way of storing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently. It is an organization of mathematical and logical concepts of data. Often a carefully chosen data structure will allow the most efficient algorithm to be used. The choice of the data structure often begins from the choice of an abstract data type.
A data model describes the structure of the data within a given domain and, by implication, the underlying structure of that domain itself. This means that a data model in fact specifies a dedicated grammar for a dedicated artificial language for that domain. A data model represents classes of entities (kinds of things) about which a company wishes to hold information, the attributes of that information, and relationships among those entities and (often implicit) relationships among those attributes. The model describes the organization of the data to some extent irrespective of how data might be represented in a computer system.
The entities represented by a data model can be the tangible entities, but models that include such concrete entity classes tend to change over time. Robust data models often identify abstractions of such entities. For example, a data model might include an entity class called "Person", representing all the people who interact with an organization. Such an abstract entity class is typically more appropriate than ones called "Vendor" or "Employee", which identify specific roles played by those people.
A data model instance is created by applying a data model theory. This is typically done to solve some business enterprise requirement. Business requirements are normally captured by a semantic logical data model. This is transformed into a physical data model instance from which is generated a physical database. For example, a data modeler may use a data modeling tool to create an entity-relationship model of the corporate data repository of some business enterprise. This model is transformed into a relational model, which in turn generates a relational database.
 A data flow diagram (DFD) is a graphical representation of the "flow" of data through an information system. It differs from the flowchart as it shows the data flow instead of the control flow of the program. A data flow diagram can also be used for the visualization of data processing (structured design). Data flow diagrams were invented by Larry Constantine, the original developer of structured design,[22] based on Martin and Estrin's "data flow graph" model of computation.
A data flow diagram (DFD) is a graphical representation of the "flow" of data through an information system. It differs from the flowchart as it shows the data flow instead of the control flow of the program. A data flow diagram can also be used for the visualization of data processing (structured design). Data flow diagrams were invented by Larry Constantine, the original developer of structured design,[22] based on Martin and Estrin's "data flow graph" model of computation.
It is common practice to draw a context-level Data flow diagram first which shows the interaction between the system and outside entities. The DFD is designed to show how a system is divided into smaller portions and to highlight the flow of data between those parts. This context-level Data flow diagram is then "exploded" to show more detail of the system being modeled
According to Lee (1999)[23] an information model is a representation of concepts, relationships, constraints, rules, and operations to specify data semantics for a chosen domain of discourse. It can provide sharable, stable, and organized structure of information requirements for the domain context.[23] More in general the term information model is used for models of individual things, such as facilities, buildings, process plants, etc. In those cases the concept is specialised to Facility Information Model, Building Information Model, Plant Information Model, etc. Such an information model is an integration of a model of the facility with the data and documents about the facility.
An information model provides formalism to the description of a problem domain without constraining how that description is mapped to an actual implementation in software. There may be many mappings of the information model. Such mappings are called data models, irrespective of whether they are object models (e.g. using UML), entity relationship models or XML schemas.
In computing the term object model has a distinct second meaning of the general properties of objects in a specific computer programming language, technology, notation or methodology that uses them. For example, the Java object model, the COM object model, or the object model of OMT. Such object models are usually defined using concepts such as class, message, inheritance, polymorphism, and encapsulation. There is an extensive literature on formalized object models as a subset of the formal semantics of programming languages.
 Object-Role Modeling (ORM) is a method for conceptual modeling, and can be used as a tool for information and rules analysis.[27]
Object-Role Modeling (ORM) is a method for conceptual modeling, and can be used as a tool for information and rules analysis.[27]
Object-Role Modeling is a fact-oriented method for performing systems analysis at the conceptual level. The quality of a database application depends critically on its design. To help ensure correctness, clarity, adaptability and productivity, information systems are best specified first at the conceptual level, using concepts and language that people can readily understand.
The conceptual design may include data, process and behavioral perspectives, and the actual DBMS used to implement the design might be based on one of many logical data models (relational, hierarchic, network, object-oriented etc.).[28]

Overview of data modeling context: Data model is based on Data, Data relationship, Data semantic and Data constraint. A data model provides the details of information to be stored, and is of primary use when the final product is the generation of computer software code for an application or the preparation of a functional specification to aid a computer software make-or-buy decision. The figure is an example of the interaction between process and data models.[1]
Precise accounting and communication is a large expense and organizations traditionally paid the cost by having employees translate between themselves on an ad hoc basis. In critical situations such as air travel, healthcare and finance, it is becoming commonplace that the accounting and communication must be precise and therefore requires the use of common data models to obviate risk.
According to Hoberman (2009), "A data model is a wayfinding tool for both business and IT professionals, which uses a set of symbols and text to precisely explain a subset of real information to improve communication within the organization and thereby lead to a more flexible and stable application environment."[2]
A data model explicitly determines the structure of data. Data models are specified in a data modeling notation, which is often graphical in form.[3]
A data model can be sometimes referred to as a data structure, especially in the context of programming languages. Data models are often complemented by function models, especially in the context of enterprise models.
Contents
[hide]Overview[edit]
Managing large quantities of structured and unstructured data is a primary function of information systems. Data models describe the structure, manipulation and integrity aspects of the data stored in data management systems such as relational databases. They typically do not describe unstructured data, such as word processing documents, email messages, pictures, digital audio, and video.The role of data models[edit]

How data models deliver benefit.[4]
- "Business rules, specific to how things are done in a particular place, are often fixed in the structure of a data model. This means that small changes in the way business is conducted lead to large changes in computer systems and interfaces".[4]
- "Entity types are often not identified, or incorrectly identified. This can lead to replication of data, data structure, and functionality, together with the attendant costs of that duplication in development and maintenance".[4]
- "Data models for different systems are arbitrarily different. The result of this is that complex interfaces are required between systems that share data. These interfaces can account for between 25-70% of the cost of current systems".[4]
- "Data cannot be shared electronically with customers and suppliers, because the structure and meaning of data has not been standardised. For example, engineering design data and drawings for process plant are still sometimes exchanged on paper".[4]
A data model explicitly determines the structure of data or structured data. Typical applications of data models include database models, design of information systems, and enabling exchange of data. Usually data models are specified in a data modeling language.[3]
Communication and precision are the two key benefits that make a data model important to applications that use and exchange data. A data model is the medium which project team members from different backgrounds and with different levels of experience can communicate with one another. Precision means that the terms and rules on a data model can be interpreted only one way and are not ambiguous.[2]
A data model can be sometimes referred to as a data structure, especially in the context of programming languages. Data models are often complemented by function models, especially in the context of enterprise models.
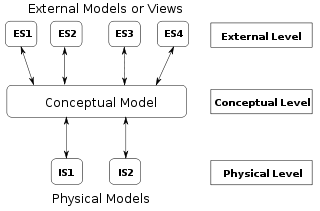
Three perspectives[edit]

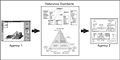
The ANSI/SPARC three level architecture. This shows that a data model can be an external model (or view), a conceptual model, or a physical model. This is not the only way to look at data models, but it is a useful way, particularly when comparing models.[4]
- Conceptual data model : describes the semantics of a domain, being the scope of the model. For example, it may be a model of the interest area of an organization or industry. This consists of entity classes, representing kinds of things of significance in the domain, and relationship assertions about associations between pairs of entity classes. A conceptual schema specifies the kinds of facts or propositions that can be expressed using the model. In that sense, it defines the allowed expressions in an artificial 'language' with a scope that is limited by the scope of the model. The use of conceptual schema has evolved to become a powerful communication tool with business users. Often called a subject area model (SAM) or high-level data model (HDM), this model is used to communicate core data concepts, rules, and definitions to a business user as part of an overall application development or enterprise initiative. The number of objects should be very small and focused on key concepts. Try to limit this model to one page, although for extremely large organizations or complex projects, the model might span two or more pages.[6]
- Logical data model : describes the semantics, as represented by a particular data manipulation technology. This consists of descriptions of tables and columns, object oriented classes, and XML tags, among other things. The logical data model captures the detailed business solution. The logical data model looks the same regardless of whether we are implementing in MongoDB or Oracle.[7]
- Physical data model : describes the physical means by which data are stored. This is concerned with partitions, CPUs, tablespaces, and the like. The physical data model is the detailed technical solution. This is the first time we are actually concerning ourselves with technology and technology issues such as performance, storage, and security.[7]
History[edit]
One of the earliest pioneering works in modelling information systems was done by Young and Kent (1958),[8][9] who argued for "a precise and abstract way of specifying the informational and time characteristics of a data processing problem". They wanted to create "a notation that should enable the analyst to organize the problem around any piece of hardware". Their work was a first effort to create an abstract specification and invariant basis for designing different alternative implementations using different hardware components. A next step in IS modelling was taken by CODASYL, an IT industry consortium formed in 1959, who essentially aimed at the same thing as Young and Kent: the development of "a proper structure for machine independent problem definition language, at the system level of data processing". This led to the development of a specific IS information algebra.[9]In the 1960s data modeling gained more significance with the initiation of the management information system (MIS) concept. According to Leondes (2002), "during that time, the information system provided the data and information for management purposes. The first generation database system, called Integrated Data Store (IDS), was designed by Charles Bachman at General Electric. Two famous database models, the network data model and the hierarchical data model, were proposed during this period of time".[10] Towards the end of the 1960s Edgar F. Codd worked out his theories of data arrangement, and proposed the relational model for database management based on first-order predicate logic.[11]
In the 1970s entity relationship modeling emerged as a new type of conceptual data modeling, originally proposed in 1976 by Peter Chen. Entity relationship models were being used in the first stage of information system design during the requirements analysis to describe information needs or the type of information that is to be stored in a database. This technique can describe any ontology, i.e., an overview and classification of concepts and their relationships, for a certain area of interest.
In the 1970s G.M. Nijssen developed "Natural Language Information Analysis Method" (NIAM) method, and developed this in the 1980s in cooperation with Terry Halpin into Object-Role Modeling (ORM).
Bill Kent, in his 1978 book Data and Reality[12] compared a data model to a map of a territory, emphasizing that in the real world, "highways are not painted red, rivers don't have county lines running down the middle, and you can't see contour lines on a mountain". In contrast to other researchers who tried to create models that were mathematically clean and elegant, Kent emphasized the essential messiness of the real world, and the task of the data modeller to create order out of chaos without excessively distorting the truth.
In the 1980s according to Jan L. Harrington (2000) "the development of the object-oriented paradigm brought about a fundamental change in the way we look at data and the procedures that operate on data. Traditionally, data and procedures have been stored separately: the data and their relationship in a database, the procedures in an application program. Object orientation, however, combined an entity's procedure with its data."[13]
Types of data models[edit]
Database model[edit]
Main article: Database model
A database model is a specification describing how a database is structured and used.Several such models have been suggested. Common models include:
- Flat model
- This may not strictly qualify as a data model. The flat (or table) model consists of a single, two-dimensional array of data elements, where all members of a given column are assumed to be similar values, and all members of a row are assumed to be related to one another.
- Hierarchical model
- In this model data is organized into a tree-like structure, implying a single upward link in each record to describe the nesting, and a sort field to keep the records in a particular order in each same-level list.
- Network model
- This model organizes data using two fundamental constructs, called records and sets. Records contain fields, and sets define one-to-many relationships between records: one owner, many members.
- Relational model
- is a database model based on first-order predicate logic. Its core idea is to describe a database as a collection of predicates over a finite set of predicate variables, describing constraints on the possible values and combinations of values.
- Object-relational model
- Similar to a relational database model, but objects, classes and inheritance are directly supported in database schemas and in the query language.
- Star schema
- The simplest style of data warehouse schema. The star schema consists of a few "fact tables" (possibly only one, justifying the name) referencing any number of "dimension tables". The star schema is considered an important special case of the snowflake schema.
Data Structure Diagram[edit]
Main article: Data structure diagram
A data structure diagram (DSD) is a diagram and data model used to describe conceptual data models by providing graphical notations which document entities and their relationships, and the constraints that bind them. The basic graphic elements of DSDs are boxes, representing entities, and arrows, representing relationships. Data structure diagrams are most useful for documenting complex data entities.Data structure diagrams are an extension of the entity-relationship model (ER model). In DSDs, attributes are specified inside the entity boxes rather than outside of them, while relationships are drawn as boxes composed of attributes which specify the constraints that bind entities together. The E-R model, while robust, doesn't provide a way to specify the constraints between relationships, and becomes visually cumbersome when representing entities with several attributes. DSDs differ from the ER model in that the ER model focuses on the relationships between different entities, whereas DSDs focus on the relationships of the elements within an entity and enable users to fully see the links and relationships between each entity.
There are several styles for representing data structure diagrams, with the notable difference in the manner of defining cardinality. The choices are between arrow heads, inverted arrow heads (crow's feet), or numerical representation of the cardinality.
Entity-relationship model[edit]
Main article: Entity-relationship model
An entity-relationship model (ERM) is an abstract conceptual data model (or semantic data model) used in software engineering to represent structured data. There are several notations used for ERMs.Geographic data model[edit]
Main article: Data model (GIS)
A data model in Geographic information systems is a mathematical construct for representing geographic objects or surfaces as data. For example,- the vector data model represents geography as collections of points, lines, and polygons;
- the raster data model represent geography as cell matrixes that store numeric values;
- and the Triangulated irregular network (TIN) data model represents geography as sets of contiguous, nonoverlapping triangles.[15]
- Groups relate to process of making a map[16]
- NGMDB data model applications[16]
- NGMDB databases linked together[16]
- Representing 3D map information[16]
Generic data model[edit]
Main article: Generic data model
Generic data models are generalizations of conventional data models. They define standardised general relation types, together with the kinds of things that may be related by such a relation type. Generic data models are developed as an approach to solve some shortcomings of conventional data models. For example, different modelers usually produce different conventional data models of the same domain. This can lead to difficulty in bringing the models of different people together and is an obstacle for data exchange and data integration. Invariably, however, this difference is attributable to different levels of abstraction in the models and differences in the kinds of facts that can be instantiated (the semantic expression capabilities of the models). The modelers need to communicate and agree on certain elements which are to be rendered more concretely, in order to make the differences less significant.Semantic data model[edit]
Main article: Semantic data model

Semantic data models.[14]
The logical data structure of a database management system (DBMS), whether hierarchical, network, or relational, cannot totally satisfy the requirements for a conceptual definition of data because it is limited in scope and biased toward the implementation strategy employed by the DBMS. Therefore, the need to define data from a conceptual view has led to the development of semantic data modeling techniques. That is, techniques to define the meaning of data within the context of its interrelationships with other data. As illustrated in the figure. The real world, in terms of resources, ideas, events, etc., are symbolically defined within physical data stores. A semantic data model is an abstraction which defines how the stored symbols relate to the real world. Thus, the model must be a true representation of the real world.[14]
Data model topics[edit]
Data architecture[edit]
Main article: Data architecture
Data architecture is the design of data for use in defining the target state and the subsequent planning needed to hit the target state. It is usually one of several architecture domains that form the pillars of an enterprise architecture or solution architecture.A data architecture describes the data structures used by a business and/or its applications. There are descriptions of data in storage and data in motion; descriptions of data stores, data groups and data items; and mappings of those data artifacts to data qualities, applications, locations etc.
Essential to realizing the target state, Data architecture describes how data is processed, stored, and utilized in a given system. It provides criteria for data processing operations that make it possible to design data flows and also control the flow of data in the system.
Data modeling[edit]
Main article: Data modeling
Data modeling in software engineering is the process of creating a data model by applying formal data model descriptions using data modeling techniques. Data modeling is a technique for defining business requirements for a database. It is sometimes called database modeling because a data model is eventually implemented in a database.[17]Data modeling is the process of learning about the data, and the data model is the end result of the data modeling process.[18]
The figure illustrates the way data models are developed and used today. A conceptual data model is developed based on the data requirements for the application that is being developed, perhaps in the context of an activity model. The data model will normally consist of entity types, attributes, relationships, integrity rules, and the definitions of those objects. This is then used as the start point for interface or database design.[4]
Data properties[edit]
Some important properties of data for which requirements need to be met are:- definition-related properties[4]
- relevance: the usefulness of the data in the context of your business.
- clarity: the availability of a clear and shared definition for the data.
- consistency: the compatibility of the same type of data from different sources.

Some important properties of data.[4]
- content-related properties
- timeliness: the availability of data at the time required and how up to date that data is.
- accuracy: how close to the truth the data is.
- properties related to both definition and content
- completeness: how much of the required data is available.
- accessibility: where, how, and to whom the data is available or not available (e.g. security).
- cost: the cost incurred in obtaining the data, and making it available for use.
Data organization[edit]
Another kind of data model describes how to organize data using a database management system or other data management technology. It describes, for example, relational tables and columns or object-oriented classes and attributes. Such a data model is sometimes referred to as the physical data model, but in the original ANSI three schema architecture, it is called "logical". In that architecture, the physical model describes the storage media (cylinders, tracks, and tablespaces). Ideally, this model is derived from the more conceptual data model described above. It may differ, however, to account for constraints like processing capacity and usage patterns.While data analysis is a common term for data modeling, the activity actually has more in common with the ideas and methods of synthesis (inferring general concepts from particular instances) than it does with analysis (identifying component concepts from more general ones). {Presumably we call ourselves systems analysts because no one can say systems synthesists.} Data modeling strives to bring the data structures of interest together into a cohesive, inseparable, whole by eliminating unnecessary data redundancies and by relating data structures with relationships.
A different approach is to use adaptive systems such as artificial neural networks that can autonomously create implicit models of data.
Data structure[edit]
Main article: Data structure

A binary tree, a simple type of branching linked data structure.
A data model describes the structure of the data within a given domain and, by implication, the underlying structure of that domain itself. This means that a data model in fact specifies a dedicated grammar for a dedicated artificial language for that domain. A data model represents classes of entities (kinds of things) about which a company wishes to hold information, the attributes of that information, and relationships among those entities and (often implicit) relationships among those attributes. The model describes the organization of the data to some extent irrespective of how data might be represented in a computer system.
The entities represented by a data model can be the tangible entities, but models that include such concrete entity classes tend to change over time. Robust data models often identify abstractions of such entities. For example, a data model might include an entity class called "Person", representing all the people who interact with an organization. Such an abstract entity class is typically more appropriate than ones called "Vendor" or "Employee", which identify specific roles played by those people.
Data model theory[edit]
The term data model can have two meanings:[19]- A data model theory, i.e. a formal description of how data may be structured and accessed.
- A data model instance, i.e. applying a data model theory to create a practical data model instance for some particular application.
- The structural part: a collection of data structures which are used to create databases representing the entities or objects modeled by the database.
- The integrity part: a collection of rules governing the constraints placed on these data structures to ensure structural integrity.
- The manipulation part: a collection of operators which can be applied to the data structures, to update and query the data contained in the database.
A data model instance is created by applying a data model theory. This is typically done to solve some business enterprise requirement. Business requirements are normally captured by a semantic logical data model. This is transformed into a physical data model instance from which is generated a physical database. For example, a data modeler may use a data modeling tool to create an entity-relationship model of the corporate data repository of some business enterprise. This model is transformed into a relational model, which in turn generates a relational database.
Patterns[edit]
Patterns[20] are common data modeling structures that occur in many data models.Related models[edit]
Data flow diagram[edit]
Main article: Data flow diagram

Data Flow Diagram example.[21]
It is common practice to draw a context-level Data flow diagram first which shows the interaction between the system and outside entities. The DFD is designed to show how a system is divided into smaller portions and to highlight the flow of data between those parts. This context-level Data flow diagram is then "exploded" to show more detail of the system being modeled
Information model[edit]
Main article: Information model
An Information model is not a type of data model, but more or less an alternative model. Within the field of software engineering both a data model and an information model can be abstract, formal representations of entity types that includes their properties, relationships and the operations that can be performed on them. The entity types in the model may be kinds of real-world objects, such as devices in a network, or they may themselves be abstract, such as for the entities used in a billing system. Typically, they are used to model a constrained domain that can be described by a closed set of entity types, properties, relationships and operations.According to Lee (1999)[23] an information model is a representation of concepts, relationships, constraints, rules, and operations to specify data semantics for a chosen domain of discourse. It can provide sharable, stable, and organized structure of information requirements for the domain context.[23] More in general the term information model is used for models of individual things, such as facilities, buildings, process plants, etc. In those cases the concept is specialised to Facility Information Model, Building Information Model, Plant Information Model, etc. Such an information model is an integration of a model of the facility with the data and documents about the facility.
An information model provides formalism to the description of a problem domain without constraining how that description is mapped to an actual implementation in software. There may be many mappings of the information model. Such mappings are called data models, irrespective of whether they are object models (e.g. using UML), entity relationship models or XML schemas.
Object model[edit]
Main article: Object model
An object model in computer science is a collection of objects or classes through which a program can examine and manipulate some specific parts of its world. In other words, the object-oriented interface to some service or system. Such an interface is said to be the object model of the represented service or system. For example, the Document Object Model (DOM) [1] is a collection of objects that represent a page in a web browser, used by script programs to examine and dynamically change the page. There is a Microsoft Excel object model[24] for controlling Microsoft Excel from another program, and the ASCOM Telescope Driver[25] is an object model for controlling an astronomical telescope.In computing the term object model has a distinct second meaning of the general properties of objects in a specific computer programming language, technology, notation or methodology that uses them. For example, the Java object model, the COM object model, or the object model of OMT. Such object models are usually defined using concepts such as class, message, inheritance, polymorphism, and encapsulation. There is an extensive literature on formalized object models as a subset of the formal semantics of programming languages.
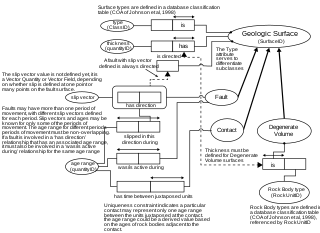
Object-Role Model[edit]
Main article: Object-Role Modeling

Example of the application of Object-Role Modeling in a "Schema for Geologic Surface", Stephen M. Richard (1999).[26]
Object-Role Modeling is a fact-oriented method for performing systems analysis at the conceptual level. The quality of a database application depends critically on its design. To help ensure correctness, clarity, adaptability and productivity, information systems are best specified first at the conceptual level, using concepts and language that people can readily understand.
The conceptual design may include data, process and behavioral perspectives, and the actual DBMS used to implement the design might be based on one of many logical data models (relational, hierarchic, network, object-oriented etc.).[28]
Unified Modeling Language models[edit]
Main article: Unified Modeling Language
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a standardized general-purpose modeling language in the field of software engineering. It is a graphical language for visualizing, specifying, constructing, and documenting the artifacts of a software-intensive system. The Unified Modeling Language offers a standard way to write a system's blueprints, including:[29]- Conceptual things such as business processes and system functions
- Concrete things such as programming language statements, database schemas, and
- Reusable software components.
See also[edit]
- Business process model
- Core Architecture Data Model
- Data dictionary
- JC3IEDM
- Process model
- Data Format Description Language (DFDL)
- Structured Search
- Key-objects
References[edit]
- Jump up ^ Paul R. Smith & Richard Sarfaty (1993). Creating a strategic plan for configuration management using Computer Aided Software Engineering (CASE) tools. Paper For 1993 National DOE/Contractors and Facilities CAD/CAE User's Group.
- Jump up ^ "Data Modeling Made Simple 2nd Edition", Steve Hoberman, Technics Publications, LLC 2009
- Jump up ^ Michael R. McCaleb (1999). "A Conceptual Data Model of Datum Systems". National Institute of Standards and Technology. August 1999.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k Matthew West and Julian Fowler (1999). Developing High Quality Data Models. The European Process Industries STEP Technical Liaison Executive (EPISTLE).
- Jump up ^ American National Standards Institute. 1975. ANSI/X3/SPARC Study Group on Data Base Management Systems; Interim Report. FDT (Bulletin of ACM SIGMOD) 7:2.
- Jump up ^ "Data Modeling for the Business", Steve Hoberman, Donna Burbank, Chris Bradley, Technics Publications, LLC 2009
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Data Modeling for MongoDB", Steve Hoberman, Technics Publications, LLC 2014
- Jump up ^ Young, J. W., and Kent, H. K. (1958). "Abstract Formulation of Data Processing Problems". In: Journal of Industrial Engineering. Nov-Dec 1958. 9(6), pp. 471-479
- ^ Jump up to: a b Janis A. Bubenko jr (2007) "From Information Algebra to Enterprise Modelling and Ontologies - a Historical Perspective on Modelling for Information Systems". In: Conceptual Modelling in Information Systems Engineering. John Krogstie et al. eds. pp 1-18
- Jump up ^ Cornelius T. Leondes (2002). Database and Data Communication Network Systems: Techniques and Applications. Page 7
- Jump up ^ "Derivability, Redundancy, and Consistency of Relations Stored in Large Data Banks", E.F. Codd, IBM Research Report, 1969
- Jump up ^ ["http://www.bkent.net/Doc/darxrp.htm" Data and Reality]
- Jump up ^ Jan L. Harrington (2000). Object-oriented Database Design Clearly Explained. p.4
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d FIPS Publication 184 released of IDEF1X by the Computer Systems Laboratory of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). 21 December 1993.
- Jump up ^ Wade, T. and Sommer, S. eds. A to Z GIS
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d David R. Soller1 and Thomas M. Berg (2003). The National Geologic Map Database Project: Overview and Progress U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 03–471.
- Jump up ^ Whitten, Jeffrey L.; Lonnie D. Bentley, Kevin C. Dittman. (2004). Systems Analysis and Design Methods. 6th edition. ISBN 0-256-19906-X.
- Jump up ^ Hoberman, Steve. (2014). Data Modeling for MongoDB. 1st edition. ISBN 9781935504702.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Beynon-Davies P. (2004). Database Systems 3rd Edition. Palgrave, Basingstoke, UK. ISBN 1-4039-1601-2
- Jump up ^ "The Data Model Resource Book: Universal Patterns for Data Modeling" Len Silverstone & Paul Agnew (2008).
- Jump up ^ John Azzolini (2000). Introduction to Systems Engineering Practices. July 2000.
- Jump up ^ W. Stevens, G. Myers, L. Constantine, "Structured Design", IBM Systems Journal, 13 (2), 115-139, 1974.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Y. Tina Lee (1999). "Information modeling from design to implementation" National Institute of Standards and Technology.
- Jump up ^ Excel Object Model Overview
- Jump up ^ "ASCOM General Requirements". 2011-05-13. Retrieved 2014-09-25.
- Jump up ^ Stephen M. Richard (1999). Geologic Concept Modeling. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 99-386.
- Jump up ^ Joachim Rossberg and Rickard Redler (2005). Pro Scalable .NET 2.0 Application Designs.. Page 27
- Jump up ^ Object Role Modeling: An Overview (msdn.microsoft.com). Retrieved 19 September 2008.
- Jump up ^ Grady Booch, Ivar Jacobson & Jim Rumbaugh (2000) OMG Unified Modeling Language Specification, Version 1.4 (2002).
Further reading[edit]
- Donna Burbank, Steve Hoberman (2011). Data Modeling Made Simple with CA ERwin Data Modeler r8. Technics Publications, LLC
- Wayne Eckerson (2011) Creating an Enterprise Data Strategy: Managing Data as a Corporate Asset
- David C. Hay (1996). Data Model Patterns: Conventions of Thought. New York:Dorset House Publishers, Inc.
- Steve Hoberman (2014). Data Modeling Master Class Training Manual 5th Edition. Technics Publications, LLC
- Steve Hoberman, Donna Burbank, & Chris Bradley (2009). Data Modeling for the Business. Technics Publications, LLC
- Steve Hoberman (2013). Data Modeling Made Simple with ER/Studio Data Architect. Technics Publications, LLC
- Steve Hoberman, George McGeachie (2011). Data Modeling Made Simple with PowerDesigner. Technics Publications, LLC
- Len Silverston (2001). The Data Model Resource Book Volume 1/2. John Wiley & Sons.
- Len Silverston & Paul Agnew (2008). The Data Model Resource Book: Universal Patterns for data Modeling Volume 3. John Wiley & Sons.
- Simsion, Graeme (2007). Data Modeling Theory and Practice. Technics Publications, LLC
- Matthew West and Julian Fowler (1999). Developing High Quality Data Models. The European Process Industries STEP Technical Liaison Executive (EPISTLE).
| ||
| ||















No comments:
Post a Comment